The Initial Public Offering (IPO) market has long been one of the most crucial elements of the global financial landscape, offering investors a chance to invest in newly listed companies and helping businesses raise capital for expansion and innovation. As the economy evolves, so too does the IPO market. Over the past few years, the dynamics of IPOs have shifted significantly, with new trends and technological advancements shaping the way companies go public and how investors approach these opportunities.
In this article, we will explore the current trends in the IPO market, offer insights for investors looking to navigate this ever-changing landscape, and examine the factors driving the evolution of IPOs. By understanding these shifts, investors can better position themselves to make informed decisions about their involvement in IPOs and capitalize on emerging opportunities.
Key Takeaways
- The IPO market is evolving with new trends, including the rise of tech IPOs, SPACs, and direct listings.
- ESG factors are becoming increasingly important for both companies and investors in the IPO space.
- Investors should focus on long-term value, diversify their investments, and stay informed about market conditions.
- Understanding new IPO structures and their potential advantages and risks is critical for successful investing in this space.
Introduction to the IPO Market
An Initial Public Offering (IPO) occurs when a privately held company offers shares of its stock to the public for the first time. This process allows the company to raise capital from a broad range of investors, which can then be used to fund expansion, reduce debt, or pursue strategic initiatives. It also marks a significant milestone in the company’s lifecycle, as it transitions from a private entity to a publicly traded one.
While the IPO process offers benefits to companies seeking growth capital, it also provides investors with an opportunity to buy into a company at an early stage, potentially benefiting from its future success. However, IPOs are not without risk, and understanding the shifting landscape of this market is critical for making sound investment decisions.
Key Trends Shaping the IPO Market
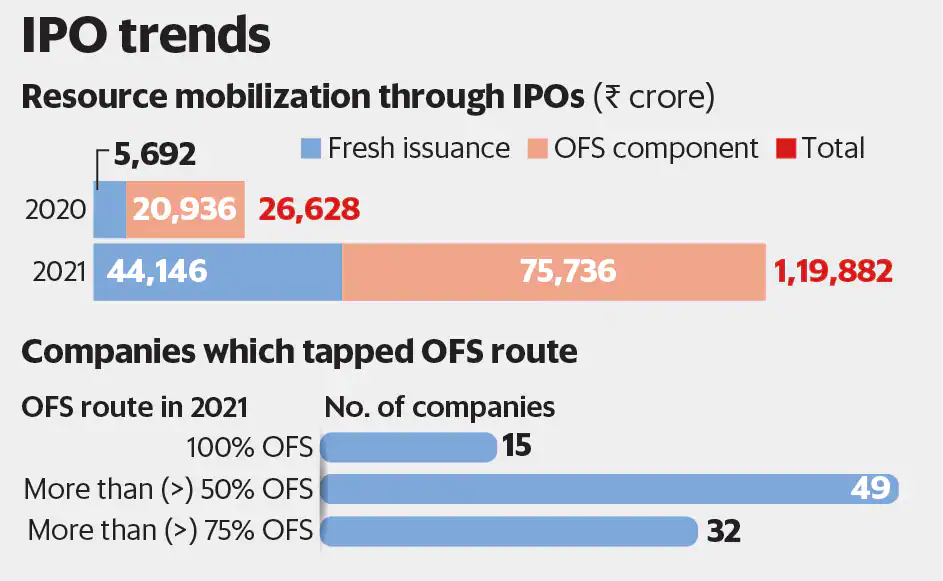
Over the past several years, several key trends have emerged that are reshaping the IPO market. These trends have altered how companies approach the IPO process and how investors assess and participate in these offerings. Let’s explore these trends in more detail.
a. The Rise of Technology and Tech IPOs
One of the most notable trends in recent years has been the surge of technology companies going public. In particular, the IPO market has seen an influx of companies from the technology, software, and fintech sectors. Companies like Facebook, Uber, and Zoom have become household names, and their IPOs have captured the attention of both retail and institutional investors.
This trend reflects the growing dominance of the technology sector in the global economy. Investors are increasingly eager to get access to the high-growth potential of tech companies, and these companies are also attracted to the IPO market to secure capital that can fuel their next stage of innovation and expansion.
In addition, the technological capabilities of these companies, combined with the rapid growth they often experience, make them highly attractive to investors. As the tech sector continues to evolve, more companies will likely explore IPOs as a means to fund further expansion and increase their market presence.
b. The Emergence of SPACs (Special Purpose Acquisition Companies)
Another significant trend that has disrupted the IPO market is the rise of SPACs. SPACs are blank-check companies that are formed with the sole purpose of raising capital through an IPO and then acquiring or merging with an existing private company, thereby taking it public.
The SPAC boom has created an alternative path to going public, bypassing the traditional IPO process. SPACs have become increasingly popular due to their speed and the ability to offer private companies a more predictable valuation and public listing. In recent years, many high-profile startups and established companies have chosen to go public via SPAC mergers rather than the traditional IPO route.
While SPACs offer a more streamlined path to going public, they have also raised concerns among some investors due to the lack of transparency and regulatory scrutiny compared to traditional IPOs. Nevertheless, SPACs continue to be a popular choice for companies seeking a faster and more flexible route to public markets.
c. The Focus on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) Criteria
Another growing trend in the IPO market is the increasing emphasis on Environmental, Social, and Governance (ESG) factors. Investors are becoming more conscious of the social and environmental impact of the companies they invest in, and they are increasingly seeking out businesses that align with their ethical values.
As a result, many companies going public today are prioritizing ESG issues as part of their corporate strategies. This includes efforts to reduce carbon emissions, promote diversity and inclusion, and adhere to strong governance standards. Investors are paying closer attention to these criteria, and businesses that can demonstrate a commitment to sustainability and social responsibility are often rewarded with greater investor interest and stronger stock performance.
This trend is expected to continue as consumer and investor expectations evolve. Companies that fail to address ESG factors may face reputational damage and difficulty attracting capital, particularly as younger generations of investors take a more active interest in sustainability.
d. The Impact of Low-Interest Rates and Market Volatility
The broader economic environment plays a significant role in shaping the IPO market, and recent conditions have led to interesting dynamics. For instance, historically low-interest rates have made it easier and cheaper for companies to raise capital through the IPO process. When interest rates are low, investors may look to equities, including IPOs, for better returns compared to bonds or other fixed-income investments.
However, the IPO market can also be influenced by market volatility. In times of market uncertainty or financial instability, companies may delay or postpone their IPO plans. The market conditions surrounding the COVID-19 pandemic are a prime example of how external factors can lead to a temporary slowdown in IPO activity. Conversely, strong market conditions and investor optimism often lead to a surge in IPOs.
For investors, these macroeconomic factors must be taken into account when considering participation in an IPO, as they can have a significant impact on the success of the offering.
e. Retail Investor Involvement and the Democratization of IPOs
In recent years, retail investors have gained more access to IPOs, thanks to technological advances and the rise of online trading platforms. Companies like Robinhood and Webull have enabled smaller investors to participate in IPOs, which were traditionally reserved for institutional investors and wealthy individuals. This democratization of IPOs has led to a broader range of market participants and has created opportunities for retail investors to engage in high-growth investment opportunities.
While this trend can provide retail investors with the opportunity to participate in exciting new offerings, it has also raised concerns about market volatility and the potential for speculative bubbles. Retail investors often lack the resources and expertise of institutional investors, and this can lead to a mismatch between demand and the actual long-term value of a company’s stock.
As more retail investors engage in IPOs, regulators may look to introduce additional protections to ensure that investors have access to the right information and are not exposed to unnecessary risks.
f. The Evolution of IPO Pricing and Valuations
Traditionally, IPO pricing was set through a process called “bookbuilding,” where underwriters would gauge investor demand to determine the final offering price. However, the way IPOs are priced has evolved in recent years. Companies and underwriters have experimented with alternative pricing methods, such as direct listings and Dutch auctions, which give investors a more direct role in setting the price of the offering.
Direct listings allow companies to bypass the traditional IPO process and go public without issuing new shares, enabling existing shareholders to sell their stock on the open market. This method can be beneficial for companies with a strong brand and established customer base, as it eliminates underwriting fees and allows for a more efficient listing process.
Dutch auctions, on the other hand, enable investors to bid for shares, with the price being set at the point where supply and demand match. This system allows for a more market-driven price discovery process and can potentially reduce the risks of underpricing that often occur in traditional IPOs.
These evolving pricing mechanisms represent a shift away from traditional IPO practices, and they may continue to gain traction as more companies explore alternative listing options.
How Investors Can Navigate the Evolving IPO Market
For investors, navigating the evolving IPO market can be both exciting and challenging. While IPOs offer the potential for significant gains, they also come with unique risks. Below are several key strategies investors can use to make the most of the opportunities presented by IPOs:
a. Conduct Thorough Research
Before investing in any IPO, it is crucial to conduct thorough research. This includes reviewing the company’s financial statements, understanding its growth potential, and assessing the competitive landscape. Investors should look for companies with a strong business model, a clear path to profitability, and a competitive advantage in their respective industries.
b. Focus on Long-Term Value
While IPOs can offer short-term gains, the true value of an investment often comes from long-term growth. It’s essential to take a long-term perspective and assess whether the company’s fundamentals are strong enough to sustain growth over time. Avoid getting caught up in the hype or speculative trends that may drive initial excitement, and instead focus on the company’s ability to create value for investors in the years to come.
c. Diversify Your IPO Investments

Diversification is always an important strategy for managing risk, and this holds true when investing in IPOs. Given the volatility and uncertainty that often accompanies newly listed companies, it’s wise to spread your investments across a range of IPOs to reduce exposure to any one individual company.
d. Consider Alternative IPO Structures
As mentioned earlier, direct listings and SPACs are becoming more common alternatives to traditional IPOs. While these structures offer advantages such as reduced costs and more flexible pricing, they also come with their own set of risks. Investors should fully understand the differences between these alternative structures and assess whether they align with their investment goals.
e. Stay Informed About Market Conditions
Market conditions, such as interest rates, economic growth, and market volatility, can significantly impact the success of IPOs. Investors should stay informed about macroeconomic trends and consider how these factors may affect the IPO market and specific companies.
Also Read: Navigating The Ipo Listing Process: What Companies Need To Know
Conclusion
The IPO market continues to evolve, shaped by trends such as the rise of technology companies, the popularity of SPACs, the increasing focus on ESG factors, and new pricing and listing methods. For investors, staying informed and understanding these trends is essential for navigating this dynamic market. By conducting thorough research, diversifying investments, and maintaining a long-term perspective, investors can capitalize on the opportunities offered by IPOs while managing the associated risks.
FAQs
What is an IPO?
An IPO is the process by which a privately held company offers shares to the public for the first time. This allows the company to raise capital and become a publicly traded entity.
What is a SPAC?
A SPAC, or Special Purpose Acquisition Company, is a publicly traded shell company formed to raise capital and acquire or merge with a private company, allowing the private company to go public.
What is a direct listing?
A direct listing allows a company to go public without issuing new shares or using underwriters. Instead, existing shareholders sell their shares directly on the stock exchange.
How do I participate in an IPO?
To participate in an IPO, investors typically need to have access to a brokerage account that offers IPO shares. Institutional investors are often prioritized, but retail investors can also participate, especially through online trading platforms.
What are the risks of investing in IPOs?
Investing in IPOs carries risks, including market volatility, the potential for overvaluation, and the lack of established performance history. It is crucial to conduct thorough research before investing.
How is an IPO price determined?
The IPO price is typically determined through a process called bookbuilding, where underwriters gauge investor demand to set the final price. Alternatively, companies may use methods like Dutch auctions or direct listings to set the price.
Can I make money from IPOs?
While IPOs have the potential for substantial gains, they are also highly speculative. Investors can make money if the company performs well, but they can also lose money if the stock underperforms after the offering.
